In the field of digital imaging, shutter technology, as the core module of exposure control, has always been the focus of optical engineering research. This article systematically sorts out the mechanisms of six major shutter technologies and their engineering applications.https://ky-ele.com/what-is-a-mechanical-shutter-a-brief-history-and-classification.html
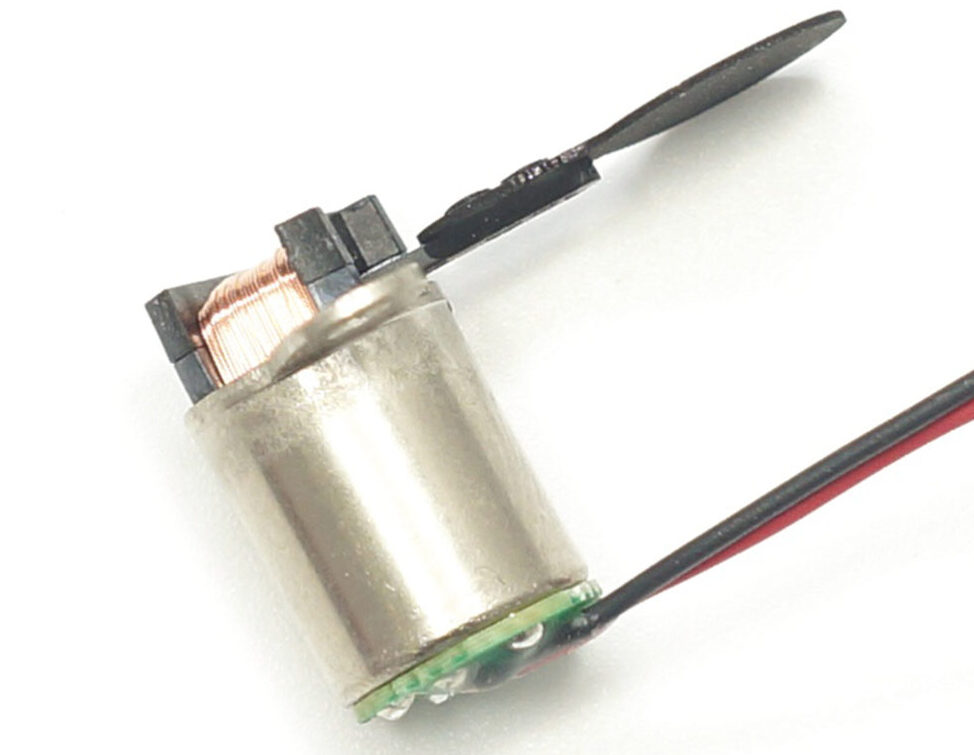
Leaf Shutter
- Structural Characteristics: Utilizes a coaxial multi-blade mechanism that opens and closes in unison.
- Optical Advantages: Maintains a constant effective aperture diameter, thereby optimizing out-of-focus image quality.
- Engineering Challenges: Requires a precise balance between high-precision synchronous control and mechanical durability.
- Typical Application: Integral component in the Phase One XT optical system.
Focal Plane Shutter
- Dynamic Model: Features a dual-curtain system that enables variable-speed scanning exposure.
- Motion Artifacts: Governed by the displacement distortion formula, Δx = v·(t₂ – t₁).
- Innovative Variant: Exemplified by Nikon Z9’s planar electromagnetic drive system.
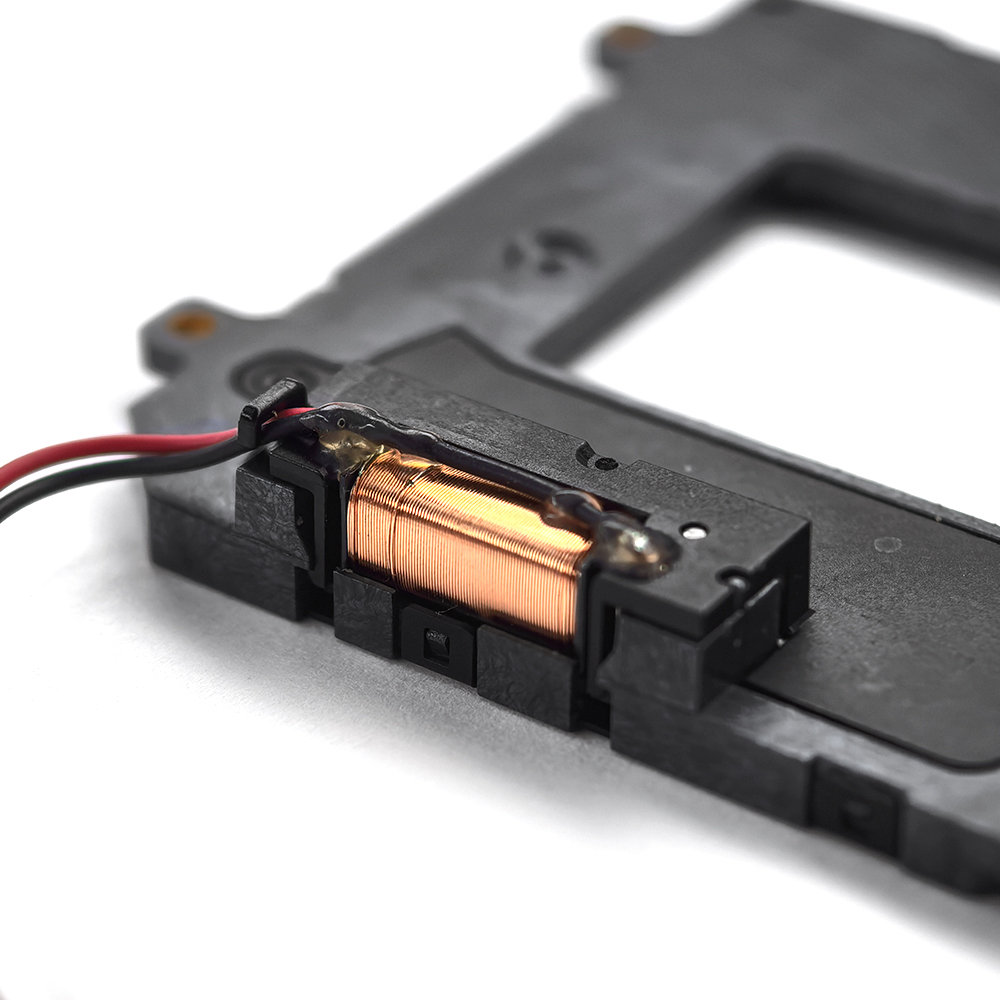
Electronic Front Curtain Shutter (EFCS)
- Hybrid Architecture: Combines an electronic reset with a mechanical curtain.
- Light Field Disturbance: Exhibits a vignetting effect due to variations in the pupil function P(x, y, t).
- Experimental Data: Demonstrated to reduce camera shake by 30% while incurring a 5% edge illuminance loss.
Rolling Shutter
- Temporal Sampling: Characterized by an inter-row exposure delay of approximately Δt ≈ 22 μs (as seen in the α7S III).
- Dynamic Distortion: Ensures stability when the condition ω·Δt < 0.1 rad is met.
- Optimization Strategy: Improved through the enhanced readout circuitry found in the Fuji X-H2S.
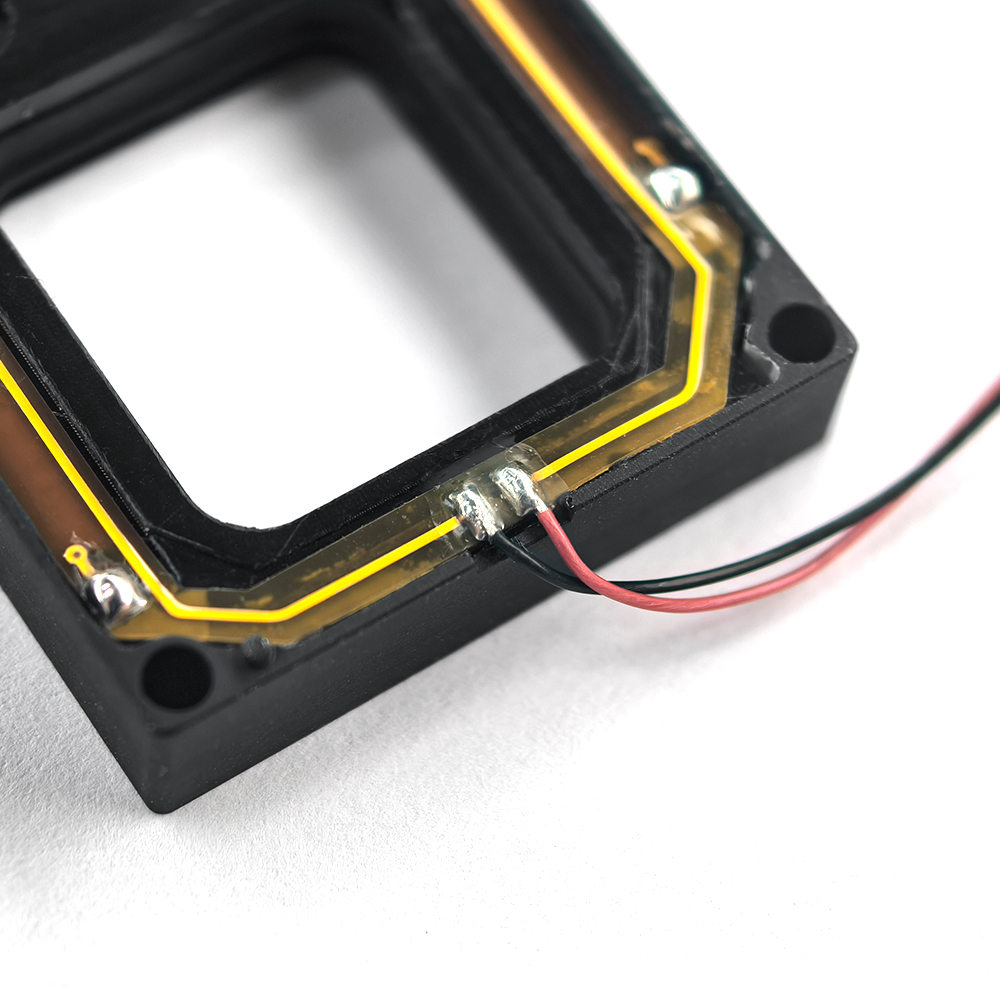
Global Shutter
- Breakthrough Progress: Notable in Sony A9III’s stacked CMOS architecture.
- Technical Metrics: Achieves pixel-level synchronization precision on the order of 1 μs.
- Application Prospects: Represents a key advancement for machine vision and light field capture.
Liquid Crystal Shutter (LC Shutter)
- Electro-Optical Properties: Based on nematic liquid crystal materials with a dielectric anisotropy of Δε = 1.5.
- Modulation Curve: The transmission function T(V) follows an S-shaped curve.
- Hybrid Scheme: Incorporated in the dual-mode shutter system proposed by our team at the 2021 EI conference.
More products can read this link:
https://kytechno.en.alibaba.com
The previous article briefly analyzed what a mechanical shutter is. If you are interested, you can read it.
What is a Mechanical Shutter? A Brief History and Classification
Technology Trend Outlook
The next generation of shutter systems is poised to evolve along three primary directions:
- Mechatronic Integration: Seamless convergence of mechanical and electronic systems.
- Multi-Physics Coupling Control: Enhanced performance through the simultaneous management of various physical phenomena.
- AI-Driven Exposure: Intelligent, adaptive exposure control leveraging artificial intelligence.
- This comprehensive analysis highlights the ongoing evolution in shutter technology and underscores its critical role in advancing modern imaging systems.
If you want to share some knowledge about optical shutter, you can communicate on our Facebook!
